Global warming, the gradual increase in the Earth’s surface temperature due to human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases, has become one of the most pressing concerns of the 21st century. Over the past few decades, scientists have warned about the consequences of rising temperatures: melting ice caps, more frequent and severe weather events, rising sea levels, and devastating impacts on ecosystems and human health. As the evidence mounts, the question arises—can global warming be reversed?
In this article, we will explore the science behind global warming, the efforts to mitigate its impact, and whether true reversal is feasible, given current technological and environmental constraints.
Understanding Global Warming
Before we dive into solutions, it’s crucial to understand the mechanisms driving global warming. At the core of the issue lies the greenhouse effect. The Earth’s atmosphere is composed of gases like carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), which trap heat from the sun. This heat keeps our planet warm enough to support life. However, since the Industrial Revolution, human activities—especially the burning of fossil fuels for energy—have significantly increased the concentration of these greenhouse gases. As a result, more heat is trapped, raising global temperatures.
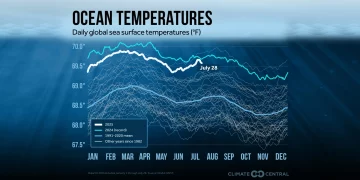
Since 1880, global average temperatures have risen by about 1.2°C (2.2°F), with the last few decades seeing accelerated warming. The consequences of this temperature rise are far-reaching: from more intense heatwaves to catastrophic storms, droughts, and wildfires. It is not just the temperature that’s changing; ecosystems, agriculture, and even human society are facing unprecedented challenges.
The Reversal Dilemma
The primary question remains: Can global warming be reversed? The short answer is no—at least not in the way many people may hope. Reversing global warming would imply completely undoing the damage done by decades of industrialization, burning fossil fuels, and deforestation. At this point, it’s unlikely that we can simply turn back the clock to pre-industrial climate conditions.
However, the situation is not entirely hopeless. While it may be impossible to reverse global warming fully, there are pathways to slow it down, mitigate its impact, and even prevent further damage. In fact, the real goal is not necessarily “reversal” but “sustainability” and a transition to a carbon-neutral world where human activities no longer contribute to further warming.
Mitigation vs. Adaptation
Before discussing solutions, it’s important to differentiate between two main strategies in combating global warming: mitigation and adaptation.

- Mitigation involves efforts to reduce or prevent the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The goal is to limit the extent of global warming, ideally to below 2°C (3.6°F) above pre-industrial levels, as outlined in the Paris Agreement.
- Adaptation, on the other hand, focuses on making adjustments to systems, practices, and policies to cope with the changing climate. This includes measures like building resilient infrastructure, improving water management, and designing crops that can thrive in hotter climates.
In the fight against global warming, both mitigation and adaptation are crucial, but the emphasis is increasingly on mitigation. The sooner we can reduce emissions and transition to cleaner, more sustainable practices, the better our chances of avoiding the worst-case scenarios.
Strategies to Slow or Reverse Global Warming
While we may not be able to reverse global warming completely, there are several promising approaches to slow down the process and reduce its impact. These strategies are broad and require concerted efforts from governments, businesses, and individuals alike.
1. Renewable Energy Transition
One of the most effective ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions is to shift away from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power all produce little to no emissions. As technology improves and costs decrease, renewable energy is becoming increasingly viable for large-scale use.
Solar energy, for example, has seen a dramatic reduction in cost over the past decade, making it one of the fastest-growing sources of power worldwide. Wind energy is similarly efficient, especially in areas with strong and consistent winds. In combination, these renewable sources could provide a substantial portion of the world’s energy needs.
The transition to renewable energy also includes the development of energy storage technologies, such as advanced batteries, that allow for intermittent power sources like solar and wind to be available even when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing.
2. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies are another promising tool in the fight against global warming. CCS involves capturing CO2 emissions from power plants, industrial sources, or directly from the air and then storing them underground or using them in various industrial applications.
Although CCS technology is still in its early stages, several pilot projects have shown promise. The key challenge is making these systems scalable and economically viable. If CCS can be deployed at a large scale, it could play a critical role in reducing atmospheric CO2 levels and even achieving negative emissions in the future.

3. Reforestation and Afforestation
Trees naturally absorb CO2 through photosynthesis, and reforestation (restoring forests that have been cut down) and afforestation (planting trees in areas where forests never existed) can significantly help in mitigating climate change. Forests are already one of the largest carbon sinks on the planet, and expanding them could capture massive amounts of CO2.
In addition to capturing carbon, forests also help regulate the water cycle, protect biodiversity, and provide habitats for wildlife. However, the scale of deforestation over the past century means that reforestation alone will not be enough to fully reverse global warming. Yet, it is still an essential part of the mitigation strategy.
4. Sustainable Agriculture
Agriculture is both a contributor to and a victim of climate change. The sector accounts for around a quarter of global greenhouse gas emissions, primarily through methane emissions from livestock and the use of synthetic fertilizers. At the same time, climate change is increasingly threatening crop yields, leading to food insecurity.
Sustainable agriculture practices, such as regenerative farming, no-till agriculture, crop rotation, and agroforestry, can help reduce emissions while improving soil health and biodiversity. By adopting more sustainable food production systems, we can reduce the carbon footprint of agriculture while ensuring that food remains abundant.
5. Geoengineering
Geoengineering refers to large-scale interventions in the Earth’s climate system to counteract global warming. While highly controversial and still in experimental stages, geoengineering technologies could play a role in mitigating the worst impacts of climate change.
Two main approaches have garnered attention:
- Solar Radiation Management (SRM): This involves reflecting some of the sun’s energy back into space using methods like aerosols in the stratosphere or artificial cloud generation. While SRM could theoretically cool the planet, it does not address the root cause of global warming—greenhouse gas emissions—and could have unintended consequences.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR): This involves directly removing CO2 from the atmosphere and storing it. This could be done through afforestation, ocean fertilization, or direct air capture (DAC). CDR holds more promise for long-term climate stabilization, but the technology is still in the early stages.
6. Lifestyle and Consumption Changes
Individual actions may not seem as powerful as large-scale technological innovations or policy changes, but they still play a significant role in reducing global warming. Shifting to a more sustainable lifestyle can reduce personal carbon footprints. This includes reducing energy consumption, eating plant-based foods, using public transport, and reducing waste.
Even small changes, when scaled globally, can have a meaningful impact. In particular, reducing meat consumption and embracing plant-based diets can significantly cut methane emissions from livestock and decrease deforestation for agriculture.
Can We Reverse the Effects of Global Warming?
While the reversal of global warming remains an unlikely goal, mitigating its effects is within our reach. We may never fully return to the climate conditions of the pre-industrial era, but it is possible to avoid the worst outcomes of unchecked climate change by acting decisively today. The future of our planet depends on the actions we take now, individually and collectively.
It is not just about mitigating the damage that has already been done, but about ensuring a sustainable future. This requires collaboration across borders, industries, and disciplines—along with the political will to act quickly and decisively.
The clock is ticking, but hope is not lost. The path to a more sustainable future is paved with innovation, responsibility, and a deep commitment to protecting the planet for future generations.